

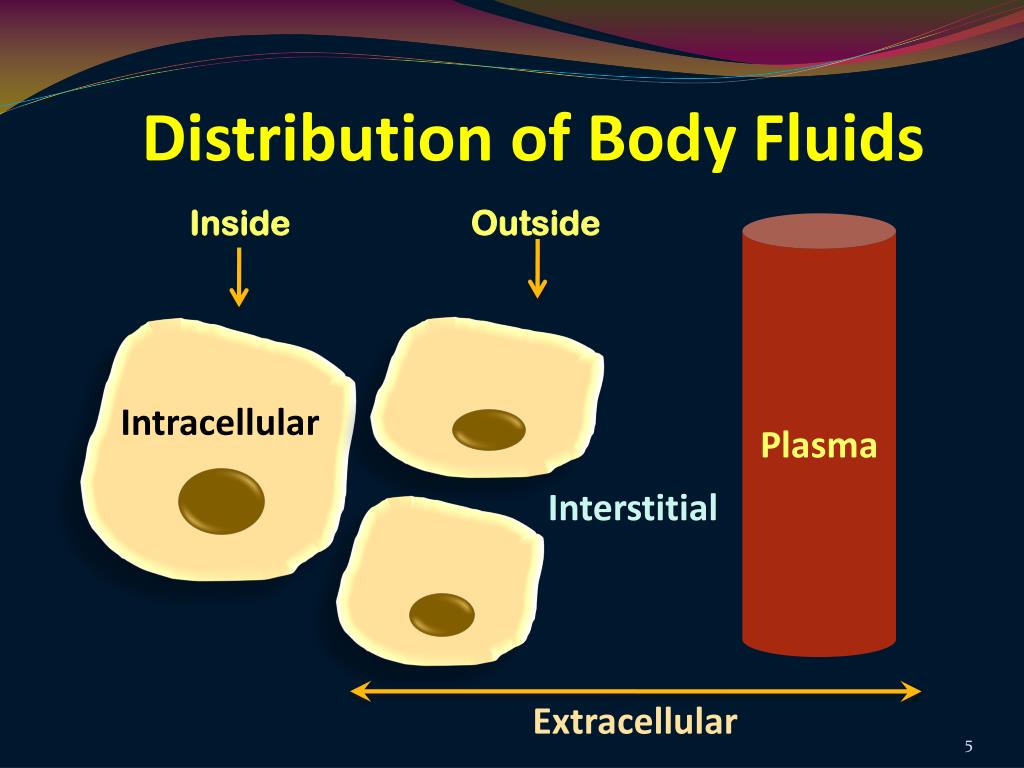
× ) and females’ lean body weight = 45.5 kg + (2.3 kg/in. calculation of volumes Properties of an Ideal Tracer The tracer should: be nontoxic be rapidly and evenly distribute throughout the nominated compartment not enter any other compartment. 2 In obese patients, it is customary to estimate TBW using lean body weight or IBW as calculated by the Devine–Devine method: males’ lean body weight = 50 kg + (2.3 kg/in. Unless the patient is obese (body weight greater than 120% of ideal body weight ), clinicians typically use a patient’s actual body weight when calculating TBW. The percentage of TBW decreases as body fat increases and/or with age (75%–85% of body weight is water for newborns). CALCULATION OF BODY FLUID COMPARTMENTS Total body water TBW 0.6 x (body weight) 0.6 x 70 Kg 42 L ICF 0.4 x (body weight) 0.4 x 70 Kg 28 L ECF 0.2 x (body weight) 0. For a typical 70 kg person, approximately 42 kg of this weight is water (which is equivalent to a volume of. For clinical purposes, most clinicians generalize that total body water accounts for 60% of lean body weight in adults, regardless of gender. This fluid is distributed between blood plasma, interstitial fluid, and Question: Background Information: Body Fluid Compartments The human body is made up of roughly 60 water with dissolved ions in various body fluid compartments. KEY CONCEPT TBW constitutes approximately 50% of lean body weight in healthy females and 60% of lean body weight in males. The most fundamental concept to grasp is an assessment of total body water (TBW), which is directly related to body weight.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
